Above ground, we’re getting ready to experience winter again. But just a few feet below the earth’s surface, the ground remains at a relatively constant temperature. Like a cave, the ground temperature is warmer than the air above during winter and cooler during summer. Geothermal heat pump systems allow you to take advantage of this constancy.
What are Geothermal Heat Pumps?
Also known as a ground source heat pump, a geothermal heat pump is a renewable energy alternative to a furnace or broiler. It has three main components:
Earth Connection Subsystem
A series of pipes connects underground that circulates fluid. This fluid could be water or a mixture of water and antifreeze. The fluid absorbs heat from (or relinquishes heat to, depending on the season) the surrounding earth.Heat Pump Subsystem
The geothermal heat pump removes the heat from the liquid in the earth connection subsystem and transfers it to the building. This process is reversed for cooling.Heat distribution subsystem
The geothermal heat pump distributes the heated or cooled air throughout the building using a conventional ductwork system.
As you can see, geothermal heat pumps act similarly to a furnace or broiler. The key difference, however, is the source of the heat. A furnace creates heat by boiling oil or gas in its combustion chamber, but a geothermal heat pump moves existing heat from the ground.
Benefits of Geothermal Heat Pump Systems
A homeowner can gain several key benefits from installing a geothermal heat pump system, including reducing their carbon footprint. Two of the most significant benefits, however, are energy efficiency and cost savings.
Energy Efficiency
Because geothermal heat pump systems don’t create heat but just transfer it from the ground, they can achieve significant energy efficiency. For all the energy delivered from a geothermal heat pump, only a fraction (about one third to one fourth) of that comes from electricity. Experts estimate that for every single unit of energy used to power a geothermal system, four units are supplied, making these systems 400% more efficient than conventional systems.
Cost Savings
It’s easy to tell how this increased energy efficiency would lead to cost savings. By reducing electricity costs and eliminating fuel costs altogether, the monthly savings alone is significant. But there are other ways geothermal heat pumps can save you money, as well, such as longevity.
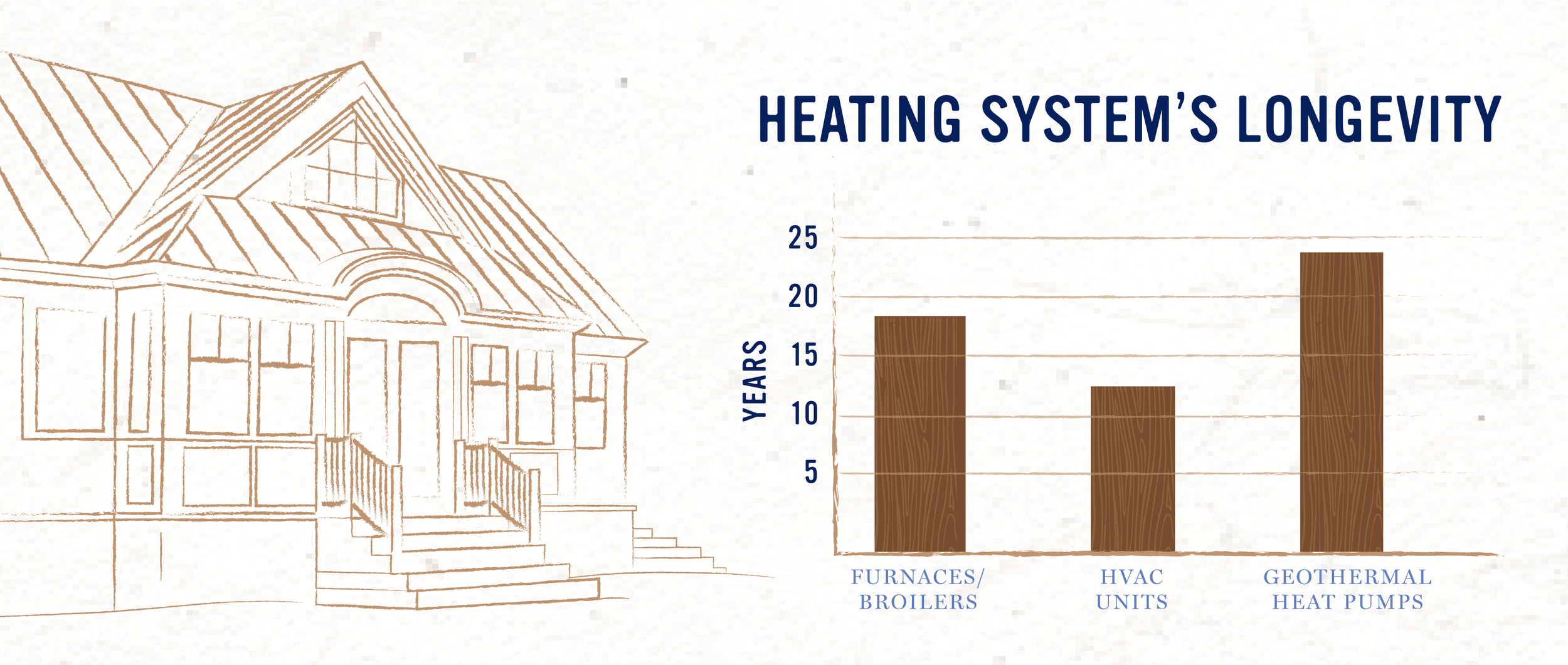
Geothermal heat pumps typically last about 20-25 years. For comparison, furnaces or broilers last about 15-20 years, and conventional HVAC units last about 10-15 years. Additionally, maintenance on geothermal systems only needs to occur every five years, whereas furnace maintenance should happen every year, and conventional HVAC units need maintenance every six months. The savings on maintenance and replacement is significant for homeowners.
Although geothermal heat pump systems are a little more costly to install upfront, once the system is installed, replacing the pump is significantly less (about one-eighth the cost) of a new HVAC unit. And since they are considered a renewable energy source, installing geothermal heat pump systems often comes with tax credits and incentives.
Request a Geothermal Heat Pump System
By utilizing heat that already exists instead of producing new heat, it’s obvious that geothermal heat pump systems are extremely beneficial to homeowners, providing them with energy efficiency and increased savings — and helping reduce their carbon footprint.
Ready to install a geothermal heat pump system? Reach out to us to discuss getting started.